What's the Character Encoding?
We always hear the words like ASCII, UTF-8, UTF-16 and Unicode when usually writing code, sometimes we call them character set or call them character encoding. What’s the relationship between them? Are they same things? And how the computer use them to store the characters? Let’s get a deep look today.
UTF-8, UTF-16, Unicode这样的名词,有时候我们称之为字符集,有时候说是字符编码。他们之间的关系到底是怎么样的呢?是不是同一样东西?计算机是如何用它们来存储字符的呢?今天我们就来一探究竟。
We all know that the computers use the binary format to store data to disks. When we want to store a character, the character has to have the corresponding binary, you can imagine it as a large mapping list, this is the character set we said. Actually, it’s a transforming algorithm the character encoding is. We use the character encoding to transform the binary of a character to a new one to save the character to disks, and inverting the binary saved in disks when reading the characters, let’s make a diagram to explain this:
字符集。 而字符编码说的是一个转换算法,就是把字符的二进制经过转换变成另一个二进制存入硬盘,读取字符时再逆向转换为字符的二进制,我们画个图来解释一下
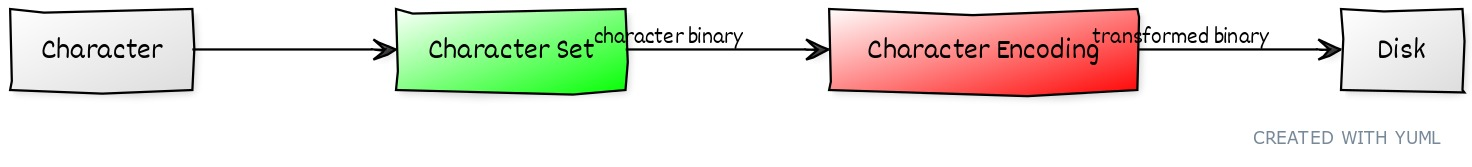
Why do we need to transform the character binary with character encoding nor storing the character binary directly? To answer this question we need to understand the evolution of the character sets following the development of the computer. As the computer was invented by American, the early character sets is applying to the Latin alphabet, the amount of Latin alphabet is 26, add later some Arabic numerals, various punctuation marks and special marks, all of them constitute the ASCII (American Standard Code for Information Interchange) set. The ASCII contains 128 characters so far, if we save them with binary, the 2^7 = 128 seven bits is just enough, but we add an extra bit in case of having another characters in the future. So there we get an interesting question why a byte has eight bits nor three or four? This is because everyone ASCII character can be referred to as an eight bits binary, the meaning of a byte is this.
character encoding再转换一遍呢?这我们就要跟着电脑的发展史来聊一聊字符集的演变。
因为计算机是由美国人发明的,所以在计算机的早期,最先建立起来的字符集就是针对拉丁字符的,拉丁字母就是 26 个英文字母,再加上后来的阿拉伯数字和各种标点符号,特殊符号,最终构成了 ASCII (American Standard Code for Information Interchange)字符集, ASCII 迄今为止总共收录了128个字符,使用二进制进行存储的话,正好是 2^7 = 128个,按理说 7 位就够了,但是为了防止以后有新的字符加入所以就多加了一位备用。这里也引出了一个有趣的问题,为什么一个字节是 8 位,不能是 3 位 4 位呢?就是因为每一个 ASCII 字符都能用 8 位二进制来表示,这也就是一个字节的含义。
Up to now we seemingly haven’t found any useful of the character encoding, actually the character set of the ASCII is its character encoding, that is to say, the ASCII hasn’t to convert. But with the development of computers, more and more countries begin using computers and every country has their own language. Like chinese has tens of thousands of characters, but the max capacity of the ASCII set is 256, clearly it’s not enough so every country begin to make their own character set, such as Europe’s ISO/IEC 8859, Japan’s Shift_Jis and China’s GB2312/GBK/BG18030. When we use the text editor of computers in the past, we have to specify the correct character encoding, otherwise you will get a bunch of messy characters. these new large character sets needs more bits to save, we might need 4 bytes or more to save the tens of thousands of chinese characters, but only the characters at the back of the character set need 4 bytes, the first bits is equal to the ASCII for compatibility with it. Some characters only need 2 bytes, if all the characters occupy 4 bytes to store, this would waste very much space and not compatible with the ASCII.
ISO/IEC 8859, 日本的 Shift_Jis,以及中国的 GB2312/GBK/GB18030 等。原来在使用电脑的文本编辑器的时候,我们需要指定使用的字符集,如果字符集错误就会出现乱码。而这些新的庞大的字符集在存储字符时就需要更多的位数,比如存储数万个中文字符,可能会需要使用 4 个字节,但是只有在字符表中靠后的字符才会用到 4 个字节,为了兼容 ASCII,前 8 位是和 ASCII 的字符集保持一致的,有些字符只需要 2 位就够了,如果都使用 4 位来存储,既不能兼容 ASCII 也会导致存储空间的大量浪费。
In order to solve the problem above, we need select different bits to save different characters. But the characters binary saved to disk is continuous, how do we determine the character needs one bit or multiple bits? This time we need to design a algorithm to resolve this question. Like GBK encoding, because the amount of collected characters isn’t very large, so we only need 1-2 bytes to save them. When saving ASCII characters, assign the highest bit of every byte to 1, so that the computer can determine the character needs one or more bits when reading them.
Later GB2312 character encoding collects more characters, so up to 4 bytes to save the characters, this needs design a more complex character encoding. The function of character encodings is to convert the fixed length binary of character sets to the variable length binary for optimize store space. The ASCII character set only need 1 bytes, so they don’t have the concept of character encoding, the GBK creator considered the character encoding when designing the character set, so the character set itself is the character encoding. And like the next Unicode character set we will talk about is a pure character set, it needs to use with a character encoding, UUF-8, UTF-6 or UTF-32. Using character sets can save some storing space, but the large character sets needs multiple calculations when converting characters, this would reduce the speed of decoding.
With computers are used in more and more countries, the more and more character sets were used, these character sets are incompatible each other, the text documents written in this computer might display a bunch of messy characters in another computers. So we urgently need a large unified character set to contain all characters, so we aren’t torn on the selections and transformations of character sets. In this expectation, the Unicode was created. The first Unicode official version was pushed in 1994, it has contained more than one million characters, the modern computer systems have supported the Unicode from the ground up, the normal software, webpage, writing articles and coding all use the Unicode.
We said that the Unicode is a pure character set above, it doesn’t support any character encoding, we can determine using the UTF-8, UTF-16 or UTF-32 depend on the storing space and performance. There are the differences between them:
- UTF-8: Variable length encoding, can use 1-6 bytes to stor a character.
- UTF-32: Fixed length encoding, every character would occupy four bytes space.
- UTF-16: Variable length encoding, using two or four bytes to store a character, this is a balanced way based on space and performance considerations.
There isn’t the best encoding way, all of them depend on the optimizations of different purposes, but with performance improvement and algorithm optimization, users are more care about the data transmission speed. The UTF-8 encoding needs the fewest bytes to transmit data, so the UTF-8 is the most popular encoding format at present. Most webpages, systems and editors use the UTF-8 as the default encoding format.
One final word, if the encoding is variable length, we say them as narrow character, eg: UTF-8. If the encoding is fixed length, we say them as wide character. Once the character encodings are complex and complicated, after generation after generation improvement, now we basically use the Unicode character set and the UTF-8 character encoding to store and transmit data.
- UTF-8: 变长的编码方案,可以使用 1-6个字节来存储字符
- UTF-32: 定长的编码方案,无论什么字符都使用 4 个字节
- UTF-16: 变长的编码方案,使用 2 个或是 4 个字节来存储,出于性能和空间的考虑,这是一种折中的方案
这里没有哪个编码方案更加的优秀,都是出于不同目的的优化,但是随着计算机性能的提升和算法的优化,在网络时代大家都更关心网络的传输速度,UTF-8 在传输数据是需要的字节最少,所以在现在 UTF-8 是使用最多的编码方案,基本上网页,系统,编辑器都是使用 UTF-8 作为默认编码。
最后再说一下,如果编码方案是变长度的,我们称之为窄字符,如 UTF-8, GBK等,如果是字符编码时定长的,我们称之为宽字符,如UTF-32, UTF-16。曾经的字符编码纷繁复杂,经过一代又一代的改进,现在我们生活中基本上就是使用基于 Unicode 字符集的 UTF-8 字符编码来存储和传输数据的。
